 Ciena, a telecom infrastructure company, and Analysys Mason said connected healthcare will be the most important driver for 5G in India.
Ciena, a telecom infrastructure company, and Analysys Mason said connected healthcare will be the most important driver for 5G in India.
The report also said telecom operators need a strong wireline phone strategy to enjoy success in 5G services in future.
Last year, Bharti Airtel and BSNL announced their 5G agreement with Finnish telecom major Nokia for exploring 5G mobile technology.
Ericsson in its recent Mobility Report said that 5G subscriptions will be available in 2022 in India — representing 0.2 percent of total mobile subscriptions reaching 3 million.
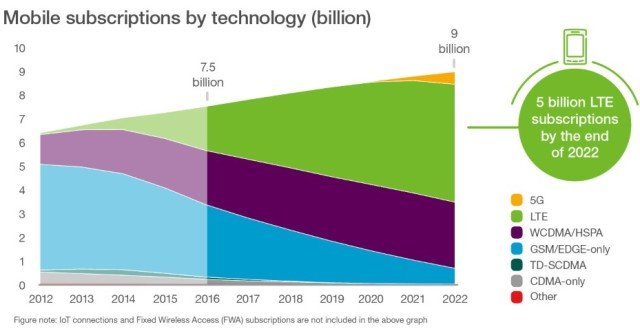 LTE 4G and WCDMA/HSPA 3G technologies together are expected to represent 85 percent of all Indian subscriptions by 2022.
LTE 4G and WCDMA/HSPA 3G technologies together are expected to represent 85 percent of all Indian subscriptions by 2022.
India had 23 million cellular IoT connections in 2016. The number of cellular IoT connections will reach 191 million by 2022.
Interestingly, during the promotion period of 4G infrastructure roll outs, 4G was also positioned as a data service for boosting digital healthcare such as e-medicine, etc. In reality, 4G LTE is supporting enterprises in boosting their connectivity needs.
Investment in wireline infrastructure is crucial for telecom operators in Asia Pacific to achieve success in supporting 5G services, according to a survey by Analysys Mason. Both BSNL and Airtel have wireline presence in India.
Incidentally, Indian telecom operators do not have a strong wireline infrastructure. State-run telecom operator BSNL is the leading wireline telecom operator in India.
Analysys Mason said less than 25 percent of MNOs surveyed have a fully integrated wireless / wireline strategy, with the majority planning both sides concurrently, yet independently.
MNOs must develop a converged holistic wireline strategy, even if plans to integrate 5G radios are still a ways off.
Ciena webinar – Impact of 5G on wireline networks
Top drivers in Asia Pacific to deploy 5G by 2023 are lower total cost of ownership (TCO), efficiency and flexibility in harnessing resources including spectrum, fiber and radio network, and support for new revenues, according to the Analysys Mason’s survey.
71 percent of MNOs in the developed Asia Pacific region are engaged in some 5G planning to launch 5G services prior to 2024. One quarter of those in emerging Asia Pacific regions have started.
MNOs cite diverse reasons for implementing 5G at an early stage (2018 to 2023) including: enhancing networks to support a high-profile event such as the Tokyo Summer Olympics, improving cost efficiency and uncovering new revenue streams.
The report said delivering new video services through enhanced broadband was cited as the most important use case in Asia Pacific. Operators in Japan are focusing on new user experiences driven by virtual reality.
Connected vehicles and the industrial Internet of Things (IoT) are key drivers in Japan and Korea, while connected healthcare is the most important driver for India, Australia, and Vietnam.
Telecom operators must prioritize improving the efficiency and flexibility of existing and future resources, using three new and intertwined approaches – NFV, SDN, and network slicing.
These technologies will help converge wireline and wireless networks and tap into both pools of capacity in an on-demand basis, share resources as flexibly as possible, and help create new revenue streams.
“Central to their strategy is integrating fiber and radio across their network architecture – a crucial element for MNOs to stay ahead of competition, transform their cost base, and provide a richer experience for their users,” said Stephen Wilson, principal analyst at Analysys Mason.
Recently, some of the Indian telecom operators said investment in fiber will be a top priority for them in the next 3 years. Indian telecoms are expected to invest nearly Rs 2 lakh crore in spectrum and telecom infrastructure in three years.
“Ciena’s approach to building networks aligns with the recommendations in the research, where we have long been an advocate of the integration of wireless and wireline technologies, and now with SDN and NFV for orchestration of the physical and virtual networks for optimal flexibility and efficiency,” said Anthony McLachlan, vice president of APAC, Ciena.
Analysys Mason analyzed the impact of 5G deployments in the Asia-Pacific region on wireline networks. The data came from a survey — conducted in the fourth quarter of 2016 — of 54 mobile networking operators in APAC. Respondents were CTOs or executives with responsibility for network planning and deployment.
Baburajan K
editor@telecomlead.com
