Telecom Lead Asia: Fujitsu, NTT and NEC have decided to conduct joint research to create 400G technology.
The joint research will enable 400Gbps-class optical transmissions through the use of dual-polarization quadrature phase shift keying (DP-QPSK), which is currently in use for 100Gbps transmissions, together with dual-polarization 16 quadrature amplitude modulation (DP-16QAM).
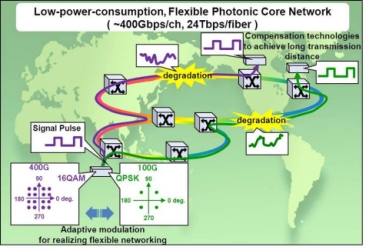
Through the new project, the companies will enable the following kinds of next-generation optical network capabilities by 2014:
1. Ultra-high-speed and high-capacity optical transmissions – 400Gbps/channel-class and 24Tbps/fiber
2. Compensation for chromatic dispersion, polarization mode dispersion and nonlinear effects occurring on a fiber-optic line, all of which are factors that lead to performance deterioration. This results in improved optical reach (greater than 2 times that of existing technologies).
3. A substantial reduction in network power consumption (less than half of existing technologies) as a result of the need for fewer devices.
4. The construction of flexible networks through adaptive modulation/demodulation using a single hardware device.
The companies will work until 2014 to address technological challenges. They will develop technologies pertaining to 400Gbps-class transmissions and low power consumption, while striving to make available the results of these efforts.
In addition, they will collaborate with institutions inside and outside Japan in an aim to deploy their achievements on a global scale.
This R&D initiative was commissioned and is sponsored by Japan’s Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications (MIC) as part of the “Research and Development Project for the Ultra-high Speed and Green Photonic Networks” program.
Fujitsu, NTT and NEC have already pursued R&D on 100Gbps-class digital coherent optical communications technology as part of the MIC’s “Research and Development on High Speed Optical Transport System Technologies” program (2009) and “Research and Development on Ultra-high Speed Optical Edge Node Technologies” program (2010-2011).
Dana Cooperson, VP Network Infrastructure, Ovum, said: “Fujitsu, NTT and NEC’s efforts to meet this growing demand illustrate what’s possible when key industry players work together. Carriers, enterprises, governments, and others would be wise to look closely at this solution as they evolve their networks.”