5G is becoming a marketing tool for several telecom operators worldwide amid concerns that it does not support ARPU growth or reduce margin pressure in the short term.
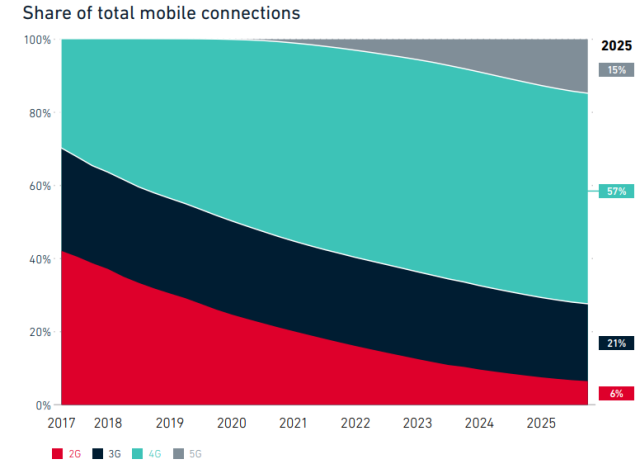 Mobile broadband and fixed-wireless broadband will be the two main uses for 5G. That shows that telecoms will be focusing on 5G-driven connectivity for consumers. This is because enterprise use cases that can power 5G revenue growth will become a reality after several years.
Mobile broadband and fixed-wireless broadband will be the two main uses for 5G. That shows that telecoms will be focusing on 5G-driven connectivity for consumers. This is because enterprise use cases that can power 5G revenue growth will become a reality after several years.
5G will be a new marketing tool for CSPs to differentiate themselves, TBR’s telecom predictions for 2019 said.
Ooredoo, a leading telecom operator in the Middle East, already announced 5G in Kuwait. But the service is not available for retail or business customers. The aim is to join the 5G bandwagon.
5G will provide an opportunity for CSPs to add market share. 4G did not support telecom operators to add market share or ARPU. In fact, ARPU fell substantially in the Indian telecom market – mainly due to competition and lack of ability of consumers to buy content from 4G mobile operators.
 Telcos will not be able to enhance ARPU from traditional connectivity services by making investment in 5G, the report said. Gains in market share will be limited until 5G devices and coverage become widely available.
Telcos will not be able to enhance ARPU from traditional connectivity services by making investment in 5G, the report said. Gains in market share will be limited until 5G devices and coverage become widely available.
Strategy Analytics said 5G smartphones in the initial phase will be too costly. Consumers in Asia and other developing nations will not be able to buy costly smartphones. The price can be more than $1,000 per 5G handset.
Cost consideration is the justification for the 5G investment. Telecom network makers say 5G is up to 10 times more efficient on a cost per gigabyte basis compared to LTE. CSPs are keen to use 5G solutions that can help them support that traffic load in the most cost-efficient way possible.
T-Mobile, the third largest telecom operator in US, signed two 5G equipment sourcing deals with Ericsson and Nokia worth $3.5 billion each.
5G investment will provide much needed revenue growth to telecom operators in the long-run after 4G fell short of this goal over the past decade, Chris Antlitz, senior analyst at TBR, said.
TBR’s telecom predictions for 2019 indicate that 5G will enable Industry 4.0, which will spur revenue generation opportunities for service providers that provide the connectivity layer and value-added services to businesses — in the long run.
5G will support commercially viable use cases for the network between 2022 and 2025. But it will not reduce existing challenges such as lack of revenue growth and margin pressure in the next few years.
Communication service providers (CSPs) will focus on cost optimization and will allocate their initial 5G investments to enhance their traditional connectivity businesses to more cost-effectively support data traffic coming onto their networks.
A GSMA report said that 5G connections will touch 50 million in the Middle East and North Africa region in 2025.
Indian telecom operator Bharti Airtel does not want to buy 5G spectrum in 2019. Airtel took early leads in both 3G and 4G network deployments as compared with other Indian telecom operators.
Vodafone Idea, another telecom in India, does not want to invest in 5G networks till 2020. The main focus of Vodafone Idea is to enhance 4G coverage by investing Rs 27,000 crore in networks.
CSPs’ spend on NFV/SDN-related initiatives will exceed $38.8 billion in 2019, nearly double the level spent in 2018. This significant increase in investment will be driven by two factors: CSPs are under pressure to realize cost savings as their connectivity businesses remain under pressure and 5G will push CSPs to pull forward their NFV/SDN road maps, TBR said.
Tier 1 telecom operators expect cost savings from 30 percent to 60 percent when comparing a traditional network environment to an NFV/SDN-centric network environment.
The bulk of the cost savings stems from the use of lower-cost, white box hardware and open source software as well as energy savings, real estate footprint reduction and automation of manually performed tasks.
5G for big telecoms
Though most CSPs intend to initially deploy the NSA standard of 5G, which tethers 5G radio with EPC, an upgrade to the SA standard, which tethers 5G radio to a 5G core, will become a reality in the early 2020s.
CSPs will be keen to prepare their networks to fully maximize the benefits from utilizing a fully virtualized network architecture, which includes, but is not limited to, increasing agility, flexibility, visibility and cost efficiency.
More CSPs are broadening their NFV/SDN initiatives or will start adopting in 2019. Verizon, T-Mobile, NTT Docomo, China Mobile, Swisscom, Telia and many others plan to increase investment in their network transformation initiatives, of which NFV and SDN are key underlying components of those initiatives.
Verizon is betting on 5G fixed wireless. More CSPs will begin to leverage their wireless assets to provide similar services in 2019 and beyond.
AT&T, with its 5G puck powered by Netgear Nighthawk 5G Mobile Hotspot provides a broadband connection leveraging 5G.
T-Mobile is also looking to jump on the bandwagon. T-Mobile intends to leverage its mix of low-, mid- and high-band spectrum assets with the wireless technologies to provide its own mobile broadband as an alternative to fixed broadband services.
4G / LTE did not work well in several telecom markets because telecom operators did not focus on enhancing mobile data speed to sell content and enterprise offerings. 5G is facing the same issue in the short-term.
Baburajan K





